An agreement was recently signed that is a key step in the return of sockeye salmon to northeast Oregon’s Wallowa Lake. Bull trout, mountain whitefish, wild rainbow trout, and possibly steelhead could also start returning to Wallowa Lake when fish passage is restored.
The Wallowa Lake Irrigation District, Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation, Nez Perce Tribe and Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife have signed an agreement regarding the release and protection of instream water from Wallowa Lake.
The agreement was a necessary step for the partners to obtain state funding to complete improvements on the Wallowa Dam.
“This is a great step forward in the rehabilitation of the Wallowa Lake Dam and the return of sockeye salmon to Wallowa Lake,” said Gov. Kate Brown. “Wallowa Lake is a special place for my family and all Oregonians. I was pleased to support this project and look forward to seeing it complete.”
HB 5030 passed by the 2019 Oregon State Legislature originally allocated $14 million in lottery funds to improve the Wallowa Lake Dam. Due to the projected decrease in revenues as a result of the coronavirus (COVID-19), Lottery Revenue Bonds will not be issued in the spring of 2021, as was originally planned. Despite funding setbacks, stakeholders remain committed to improving Wallowa Lake Dam and hope funding for the project will be revisited this year or in a future legislative session.
The group has been working since November 2019 to finalize the instream water agreement; however, parties have been working for decades before that on the water supply and fisheries challenges in the basin.
“This process was truly a unique opportunity to work collaboratively with the basin to provide meaningful instream water benefits,” said Anna Pakenham Stevenson, ODFW Water Program Manager.
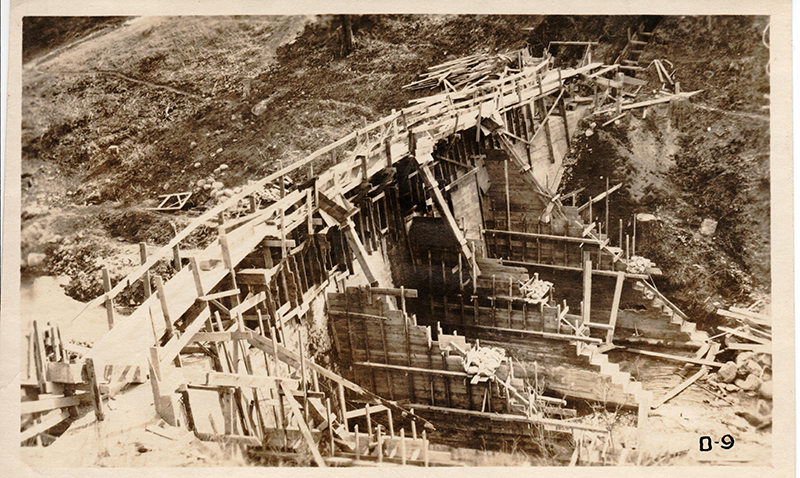
Wallowa Lake Dam was originally constructed in 1919 and does not meet current dam safety standards, putting at risk the downstream communities of Joseph, Enterprise and Wallowa.
Due to this risk, it has operated at a reduced water storage capacity since the 1990s. When it was built, the dam did not provide fish passage, which was one factor in the extinction of sockeye runs at Wallowa Lake, Oregon’s only sockeye run in the Snake River basin.
“The Parties worked together with a shared purpose to generate creative outcomes that benefitted local communities, farmers and restoration of native fisheries. Despite the current hold on funding, we will continue to build on this momentum towards making a rehabilitated dam and fish passage facilities a reality,” said Jeff Yanke, ODFW Grande Ronde District Manager.
“The agreement will help secure infrastructure for farmers and ranchers in the county, as well as contribute to the ecological health for fish and wildlife throughout the valley. This is a vital piece of infrastructure to our county, and has been an ongoing project for generations in the valley,” said Dan Butterfield, President, Wallowa Lake Irrigation District Board of Directors.
The rehabilitation project will modify the dam by improving the spillway, restoring the structural integrity, replacing the five conduit gates with new gates and upgrading the electrical and instrumentation. The rehabilitated dam will provide flood protection to local communities, more water to irrigators, the possibility of hydropower development, potable water for local communities and a host of other benefits.
“This project will ecologically reconnect Wallowa Lake to its river and protect flows in a basin critical to the many resources the Nez Perce people have used and relied upon in this area since time immemorial. The Nez Perce Tribe is pleased to see how the collaboration of different parties is moving a long-standing project closer to completion,” said Shannon Wheeler, Chairman of the Nez Perce Tribal Executive Committee.
In addition to the project addressing public safety concerns associated with the structure and reclaiming stored water rights, the instream water agreement provides unique instream flow and irrigation benefits through the Wallowa Valley.
According to the instream water agreement, up to 5000 acre-feet of water will be released from Wallowa Lake Dam annually. Of that, 4500 AF is dedicated to increasing in-stream flows in the Wallowa and Grande Ronde Rivers to the Oregon-Washington Stateline. Partners also allocated up to 500 AF for unique water trades, where irrigators trade existing surface water rights from tributaries of the Wallowa River for more reliable water rights from Wallowa Lake. The result of the water trades will leave more surface water in flow-limited tributaries.
Rehabilitating the dam will trigger the state of Oregon’s fish passage rules, and require that the dam owners provide a means of fish passage. Bull trout, mountain whitefish, wild rainbow trout, and possibly steelhead could start returning to Wallowa Lake when fish passage is restored.
But one of the key aspects of the project for fisheries co-managers is the possibility of restoring sockeye salmon back to Wallowa Lake.
“It has long been a policy goal of the Umatilla Tribes to see sockeye restored to Wallowa Lake, as well as passage for other native fish,” said Kat Brigham, Chair of the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation. “Many of our members rely on sockeye salmon for cultural and subsistence purposes. We appreciate that this agreement is a step in the right direction in these difficult times and will work for more progress when our economy improves.”
Before the dam was built, tens of thousands of sockeye returned to Wallowa Lake each year to spawn in the gravels at the river inlet on the south side of lake, and were important for Native American tribes. While kokanee (land-locked salmon) remain today, even these are mostly descendants of stocked fish.
Increased flows in the Wallowa River and potentially in important spawning tributaries as a result of restoring the dam and the flows provided under this agreement will also improve wildlife habitat and benefit other local fish and wildlife.
While the exact type of fish passage and other issues are still to be decided, stakeholders say they remain committed to the Wallowa Lake Rehabilitation Project, and expressed hope legislators can renew the state’s financial commitment when the budget stabilizes.
Also see:
— CBB, Feb. 1. 2019, IF FUNDING SURVIVES, WALLOWA LAKE DAM RECONSTRUCTION WITH FISH PASSAGE COULD BE COMPLETED IN 2021 https://www.www.www.cbbulletin.com/if-funding-survives-wallowa-lake-dam-reconstruction-with-fish-passage-could-be-completed-in-2021/
— CBB, Jan. 18, 2019, A WALLOWA LAKE DAM REPLACEMENT COULD OPEN POSSIBILITY OF SOCKEYE SALMON REINTRODUCTION https://www.www.www.cbbulletin.com/a-wallowa-lake-dam-replacement-could-open-possibility-of-sockeye-salmon-reintroduction/
— Oct. 26, 2018, FUNDRAISING UNDERWAY TO PURCHASE EASEMENT KEY TO RETURNING SOCKEYE SALMON TO WALLOWA LAKE https://www.www.www.cbbulletin.com/fundraising-underway-to-purchase-easement-key-to-returning-sockeye-salmon-to-wallowa-lake/